|
|
 |
Establishing a bull call spread involves the purchase of a call option on a particular
underlying stock, while simultaneously writing a call option on the same underlying
stock with the same expiration month, at a higher strike price. Both the buy and the sell sides
of this spread are opening transactions, and are always the same number of contracts. This
spread is sometimes more broadly categorized as a "vertical spread": a family of spreads involving
options of the same stock, same expiration month, but different strike prices. They can be created
with either all calls or all puts, and be bullish or bearish. The bull call spread, as any spread,
can be executed as a "unit" in one single transaction, not as separate buy and sell transactions.
For this bullish vertical spread, a bid and offer for the whole package can be requested through your brokerage firm from
an exchange where the options are listed and traded.

MARKET OPINION: Moderately bullish to bullish.



Moderately Bullish
An investor often employs the bull call spread in moderately bullish market
environments, and wants to capitalize on a modest advance in price of the underlying
stock. If the investor's opinion is very bullish on a stock it will generally prove more profitable
to make a simple call purchase.
Risk Reduction
An investor will also turn to this spread when there is discomfort with
either the cost of purchasing and holding the long call alone, or with the conviction of
his bullish market opinion.



The bull call spread can be considered a doubly hedged strategy. The price
paid for the call with the lower strike price is partially offset by the premium received
from writing the call with a higher strike price. Thus, the investor's investment in the long call,
and the risk of losing the entire premium paid for it, is reduced or hedged.
On the other hand, the long call with the lower strike price caps or hedges
the financial risk of the written call with the higher strike price. If the investor is assigned
an exercise notice on the written call and must sell an equivalent number of underlying shares at
the strike price, those shares can be purchased at a predetermined price by exercising the purchased
call with the lower strike price. As a trade-off for the hedge it offers, this written
call limits the potential maximum profit for the strategy.



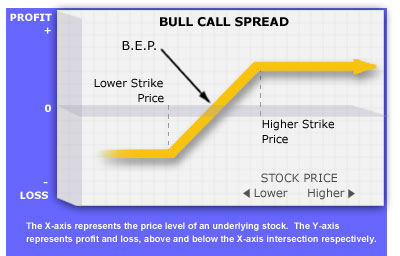
Upside Maximum Profit: Limited
Difference Between Strike Prices - Net Debit Paid
Maximum Loss: Limited
Net Debit Paid
A bull call spread tends to be profitable when the underlying stock increases
in price. It can be established in one transaction, but always at a debit
(net cash outflow). The call with the lower strike price will always be purchased at a price greater than the offsetting
premium received from writing the call with the higher strike price.
Maximum loss for this spread will generally occur as the underlying stock price
declines below the lower strike price. If both options expire out-of-the-money with no
value, the entire net debit paid for the spread will be lost. The
maximum profit for this spread will generally occur as the underlying
stock price rises above the higher strike price, and both options expire in-the-money. The investor
can exercise the long call, buy stock at its lower strike price, and sell that stock at the
written call's higher strike price if assigned an exercise notice. This will be the case no matter how high
the underlying stock has risen in price. If the underlying stock price is in between the strike
prices when the calls expire, the long call will be in-the-money and worth its intrinsic value. The
written call will be out-of-the-money, and have no value.



BEP:
Strike Price of Purchased Call + Net Debit Paid



Volatility Increases: Effect Varies
Volatility Decreases: Effect Varies
The effect of an increase or decrease in the volatility of the underlying
stock may be noticed in the time value portion of the options' premiums. The net effect on the
strategy will depend on whether the long and/or short options are in-the-money or out-of-the-money,
and the time remaining until expiration.



Passage of Time: Effect Varies
The effect of time decay on this strategy varies with the underlying stock's price level in
relation to the strike prices of the long and short options. If the stock
price is midway between the strike prices, the effect can be minimal. If the stock price
is closer to the lower strike price of the long call, losses generally increase at a faster rate
as time passes. Alternatively, if the underlying stock price is closer to the higher strike
price of the written call, profits generally increase at a faster rate as time passes.



A bull call spread purchased as a unit for a net debit in one transaction
can be sold as a unit in one transaction in the options marketplace for a credit, if it has
value. This is generally the manner in which investors close out a spread before its options expire,
in order to cut a loss or realize profit.



If both options have value, investors will generally close out a spread in
the marketplace as the options expire. This will be less expensive than incurring the commissions
and transaction costs from a transfer of stock resulting from either an exercise of and/or
an assignment on the calls. If only the purchased call is in-the-money as it expires, the investor
can either sell it in the marketplace if it has value or exercise the
call and purchase an equivalent number of shares. In either of these cases, the transaction(s) must occur before the close
of the market on the options' last trading day.
|
|
|
|